Fluorescence-guided imaging techniques, particularly when applied with the new IMAGE1 S camera system, have shown to be valuable auxiliary modalities of visualization that can be used effectively in the surgeon’s decision-making on a regular basis.
“This webpage content is intended for Healthcare Professional only, not for general public”

Please visit www.karlstorz.com for more information.
NIR/ICG fluorescence imaging with the KARL STORZ modular system solution
Using the fluorescent dye indocyanine green (ICG)* and light in the near infrared (NIR) range, KARL STORZ offers the NIR/ICG system for brilliant, laser-free FULL HD imaging of the vascular system, biliary tract, and lymphatic system. The NIR/ICG system is based on the IMAGE1 S camera platform.
- NEW: 5 mm telescope now available
- Multidisciplinary applications, for instance in general and visceral surgery, thoracic surgery, gynecology, urology, and reconstructive surgery
- Xenon-based technology (no laser protection required)
- Optimal illumination and contrast enhancement
- All-in-one solution for laparoscopic and open surgery (VITOM® II ICG)
- Outstanding user friendliness
*Please verify that the fluorescent dye indocyanine green is approved for the respective indication in your country.
Visualizing blood perfusion
Assessing the perfusion of a colon section is quick and easy with the NIR/ICG system from KARL STORZ. The monitoring of the rapid influx of ICG in the tissue allows the easy identification of the ischemic areas. Doctors using the system feel assured of their decisions.
- Direct intraoperative diagnosis decreases surgery time
- Rapid perfusion assessment of the intended resection zone
- Perfusion problems can be identified by ICG which can be utilized for resection
- Visualization of structural landmarks below the tissue surface in real-time
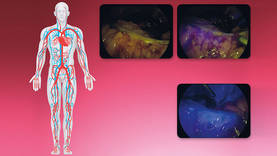
Blood perfusion assessment of colon section in a colorectal cancer patient – Source: Prof. Luigi Boni, University of Insubria, Varese, Italy
Visualizing of the biliary system
Intravenously administered ICG naturally collects in the biliary system. The collected ICG can be fluorescently excited with the NIR/ICG system from KARL STORZ, resulting in rapid identification of the biliary system anatomy. Switching between white light and fluorescence modes is performed at the touch of a button and cholecystectomies can be performed easily in a laparoscopic or open-surgical approach.
-
Shortened operation time with ICG compared to intraoperative cholangiography
-
Biliary tree mapping with ICG guidance makes the rapid delineation of the cystic duct, common bile duct and Portal vein possible
-
Intraoperative detection of bile leakage
-
Open and minimally invasive interventions can be undertaken seamlessly as only the telescopes, and not the entire camera system, need to be exchanged
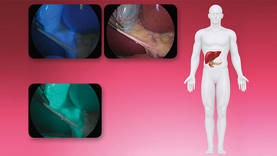
Fluorescence cholangiography during a cholecystectomy – Source: Prof. Luigi Boni, University of Insubria, Varese, Italy
Visualizing the lymphatic system
Visualizing the lymphatic system can be very helpful in many areas. The NIR/ICG system from KARL STORZ enables visualization of ICG through the lymphatic system. Doctors using the system appreciate the visual control and guidance of this fluorescence technique.
- NIR allows the intraoperative detection of sentinel lymph nodes and the lymphatic system network
- Radiation-free fluorescence guidance technique is used to predict metastatic migration through the lymphatic system
- Makes en-bloc resection of lymph nodes easier
- High node detection rates compared to established methods of lymph node visualization
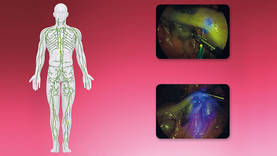
Laparoscopic transverse colectomy with fluorescence-guided lymphadenectomy – Source: Prof. Luigi Boni, University of Insubria, Varese, Italy
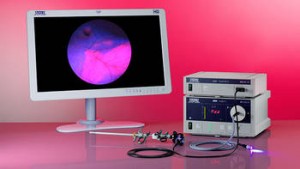
Photodynamic diagnostics (PDD)
Special features:
- Complete PDD system for diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up care
- Outstanding image quality in the flexible and rigid system as well as in white light and
PDD modes - Cost efficiency through compatible components and customer-oriented solutions
- User safety through the PDD-QAT
Additional Information:
Features that are invisible under regular light can be visualized with blue light using specially modified endoscopes.
Photodynamic diagnostics (PDD) allows visually differentiating malignant changes from healthy tissue at an early stage. For this purpose, light of a special spectral range is guided into the body through a nearly loss-free optical fiber system.
The D-LIGHT C light source is a key element of the PDD unit. After instilling a tumor marker substance, malignant tissue can be differentiated from benign tissue in the fluorescence mode: cancerous areas in the bladder fluoresce red when exposed to the stimulation light from the D-LIGHT C system. This facilitates the detection of flat neoplastic lesions such as dysplasias and carcinoma in situ, which can be concealed by normal or unspecifically inflamed mucus membranes, as well as small papillary tumors. White light alone does not achieve such differentiation, and consequently such early findings may be overlooked.
KARL STORZ started selling the first system for photodynamic diagnostics as early as 1995. Systems consist of precisely harmonized components: the high performance light source D-LIGHT C, special telescopes, and a particularly light-sensitive endoscopy camera. PDD relies on suitable and approved marker substances.
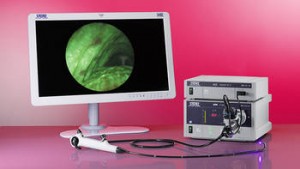
Autofluorescence (AF)
Special Features:
- Excellent image quality in both examination modes – thanks to modern CCD video chip technology and integrated auto-focus function
- Optimal gliding movement of the distal tip that responds exactly to controls – thanks to the robust design of the insertion sheath using high-quality materials
- Accurate and user-friendly work during an intervention – thanks to the ergonomic handle design and the particularly light overall weight
- Rapid changeover between white light and autofluorescence modes – thanks to convenient activation of the function keys
Additional Information:
Autofluorescence (AF) can differentiate even early malignant changes from benign tissue. The autofluorescence technique is based on the fact that some substances in the submucosa fluoresce when exposed to light of a certain wavelength. Pathological findings are visible as dark areas against an apple-green background (normal tissue).
Features that are invisible under regular light can be visualized with blue light using specially modified endoscopes. For this purpose, light of a special spectral range is guided into the body through a nearly loss-free optical fiber system. The system’s major advantage is the fact that it does not require marker substances. One of its applications is the early diagnosis of bronchial cancer.
The D-LIGHT C/AF light source is a key element of the KARL STORZ AF unit. In the fluorescence mode, malignant and benign tissue can be differentiated.
AF is used in ENT, bronchoscopy, laparoscopy, and for gynecological indications.